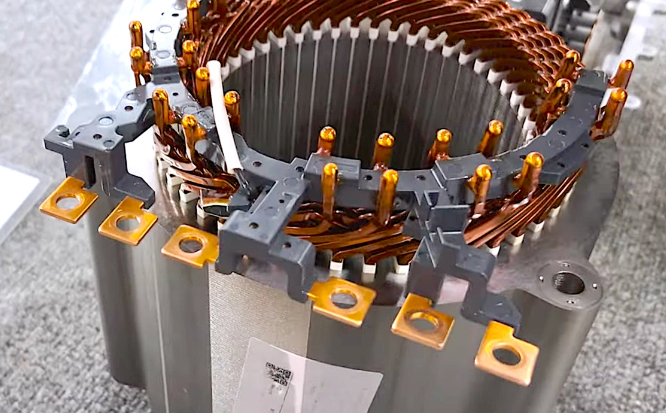
Three-phase motors have an efficiency above 90%, and together with frequency converters, precise speed control may be realized that reduces energy consumption by up to 15% to 40%. The starting current may be reduced to reduce electricity costs by 10% to 15% while reducing mechanical wear on the equipment, extending the life span, and reducing operating costs.
Improve Operating Efficiency
Three-phase motors have a significantly highly efficient design, usually over 90%. This efficiency will directly convert into savings in terms of electricity expenses. In certain industries, the savings due to the three-phase motors is $20,000 per year. During changes in the load, the running speed of the three-phase motors is constant. This feature is of crucial importance for industrial production. The efficiency also does not show major variations during variable load conditions; therefore, it ensures continuous and effortless production. Energy economy can vary from 10% to 30% more in three-phase motors than in single-phase motors for different applications.
A combination of frequency converters with three-phase motors allows for much finer speed regulation, thereby reducing energy consumption by 15% to 40%. The service life of three-phase motors is longer compared to other types of motors and generally exceeds 15 years, reducing how often a motor needs to be replaced, hence reducing maintenance costs and adding to the economic advantages. It is possible to save more than 25% on maintenance costs, which companies can invest in production research and development.

Precise Speed Control
Large groups of three-phase motors working in conjunction with frequency converters can achieve extremely high accuracy in speed control, while the motor speed is usually within the 0-100% range. Therefore, industrial equipment may automatically adjust operating speed in accordance with actual load demands without pointless energy consumption. Enterprises can reduce energy consumption by 15% to 40% after adopting variable frequency speed control. Three-phase motors can maintain ideal speed in various production stages and thus optimize product quality and production stability.
Stable operating speeds can raise product qualification rates and reduce non-conforming product costs, generally saving about 5% to 10% on raw material costs. The other benefit of accurate speed control is that it reduces shock load at the starting-up and shutting-down of the equipment, resulting in reduced impact on the power grid and less wear on the equipment. Experts point out that with this adoption, maintenance costs could be reduced by about 20%.
Reduce Starting Current
The starting current of three-phase motors is commonly three to five times the rated current, something very common in the case of traditional motors. Employing soft-start devices reduces it to 1.5 times the rated current and will considerably ease the pressure on the power grid. This reduced starting method enables enterprises to control power demand effectively. In certain situations, reducing the starting current can cut electricity costs by 10% to 15%. In fact, in many industrial applications, reducing the starting current protects motors and related equipment from damage and failures due to surges in current.
The reduction in starting current is directly reflected in the stability of the power grid, a fact especially significant at times of peak electricity usage. Many power companies actually encourage users to use low starting current motors in order to alleviate grid load and obtain corresponding reductions in electricity. Strategies to reduce the starting current when using three-phase motors have the added advantage of increasing motor service life by more than 20%. This technology is most common in the petrochemical and mining sectors, where machinery starts and stops frequently; the current drawn at startup can, therefore, be reduced effectively to lower the wear on equipment.
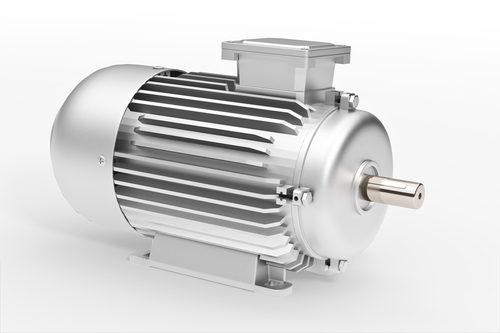
Reduce Mechanical Wear
Smooth operations importantly reduce the mechanical wear of three-phase motors, which will be very important for prolonging the service life of equipment. According to research by industrial sectors, stable operation modes can reduce equipment wear rates by 20% to 30%. It saves not only expenditures on repairing or replacing parts but also reduces the frequency of parts replacement, thereby improving economic efficiency on the whole. The continuous running capability provided by the three-phase motors enables many manufacturing enterprises to make their production process much smoother.
The design philosophy of three-phase motors underlines a reduction of vibration and noise, which directly relates to the degree of mechanical wear. In one large power equipment production plant, the MTBF improved by 25% after the application of three-phase motors. Obviously, a longer time between failures increases the availability of apparatus, therefore improving production effectiveness. A reduction in mechanical wear will increase not only the service life but also the overall effectiveness of the operation.
Reduce Thermal Loss
Three-phase motors enhance heat dissipation and, consequently, reduce thermal loss, which is normally controlled within less than 5% of rated power. Compared to traditional motors, the efficiency of three-phase motors has been enhanced by about 10%-15%. In this context, it means lesser conversion of energy into heat, thus economizing on electricity costs. It was after the introduction of three-phase motors that the energy consumption by enterprises went down 20%, and from this data, it is evident that with a reduction in thermal loss, there is a great decline in overall operating costs.
Industrial experts prove that with decreased thermal loss, equipment operational efficiency increases directly, thus enabling motors to run at even lower temperatures in a stable state and prolonging their lives. Many enterprises think that three-phase motors increase the life span by 15% to 20% compared to ordinary ones. Many three-phase motors are designed to withstand heat when working at high temperatures. For example, in the chemical industry, it has been noted that many firms have reported against high-temperature conditions of operation, in which competitive products’ three-phase motors have better thermal stability, enabling them to maintain efficient operation even in a harsh environment.