Bearing in three-phase motor supports rotor, reduces friction and protects smooth running. Regular checking of the lubrication status may replace worn-out ones in proper time to effectively prolong the service life of motors.
What is Bearing
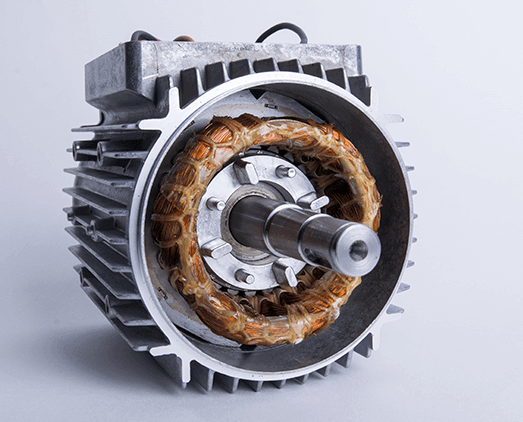
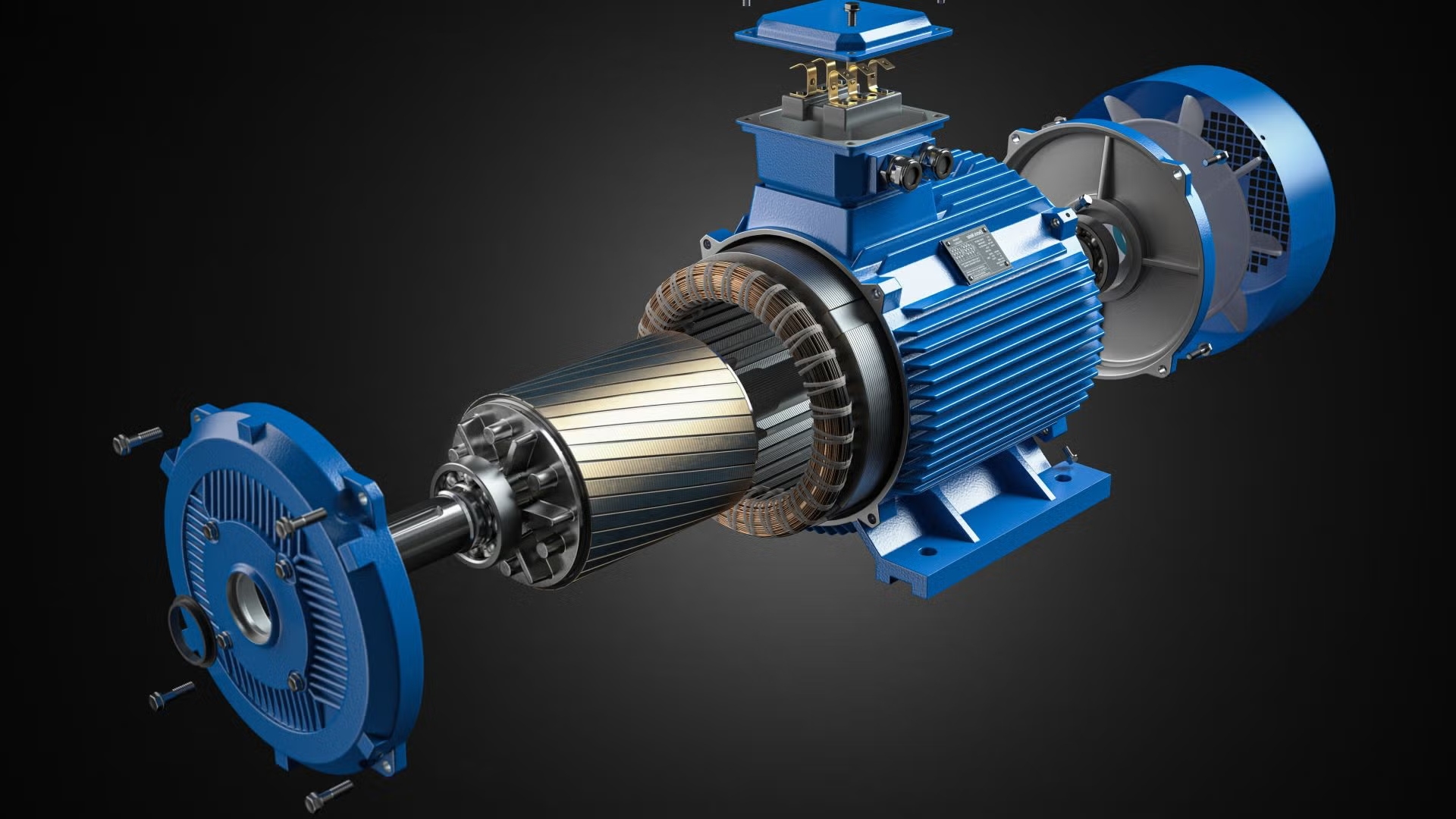
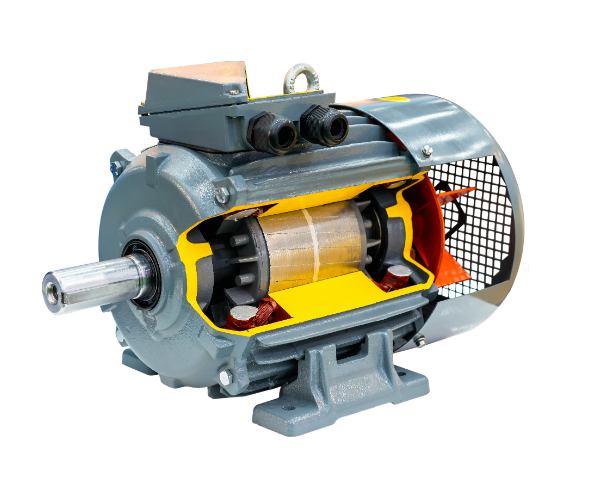
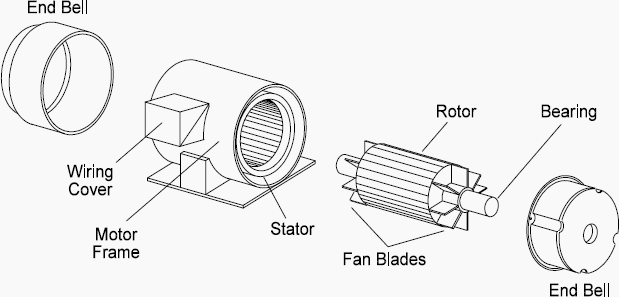
The bearing is the mechanical element that supports rotating parts and in turn reduces friction for smoothly executable rotation. Now, in the case of a three-phase motor, it is the rotor that the bearing primarily supports, allowing smooth rotation with speed. A bearing basically consists of one inner ring, one outer ring, rolling elements, and a cage. In rolling elements-balls or rollers-the contact between the inner and outer rings becomes quite negligible.
The principle of bearings is very simple: to turn sliding friction into rolling friction with minimal energy loss. The resistance due to rolling friction is usually much smaller compared to sliding friction; hence, bearings can effectively increase mechanical efficiency. Since motors involve components that rotate at high speed, the effectiveness of bearings in reducing frictional heat generation and wear plays a key role in guaranteeing long-term stability for motors.
Motor Bearings Role
While one may think that in a three-phase induction motor, the bearings perform duties like friction reduction and supporting the rotating parts, they also contribute to maintaining the stability of the motor structure internally. They support the fixing of the rotor and keep it accurately spaced from the stator, avoiding displacement or collision at times of high-speed operation. This is very important when motors operate at high speeds, since small deviations can cause friction between the rotor and stator that could damage the motor.
These bearings further permit the motor to take up radial and axial loads. The radial load refers to forces applied in the radial direction of the bearing, while axial loads are forces applied through the axial direction of the bearing. These forces taken up ensure that the rotor can rotate smoothly in a steady position. At the same time, bearings provide critical support in high-power three-phase motors.
Due to the operation of starting and stopping of a motor, huge inertia and vibration are produced. The bearings would help in absorbing and cushioning such stresses, hence reducing the impact on other mechanical components. In a modern three-phase motor, it may be noted that there are precision-designed bearings for at least mechanical vibration and noise during a particular operation. A motor shall work without any problem with high load or speed.
The good state of the bearings is what basically determines motor efficiency. The motor efficiency could be reduced by 10% to 20% by the faultiness or damage to the bearings, and this frequent replacement of bearings increases the equipment downtime by many times. The bearing, therefore, plays a very important role in the motor, not only providing mechanical support but directly influencing the performance and economic efficiency of the motor.
Types of Bearings
Different kinds of bearings work for different kinds of applications in motors: common types include ball bearings, roller bearings, spherical roller bearings, and thrust bearings. Each one of those has been designed for the specific mechanical handling of stresses and conditions; hence, the selection shall be based on such factors as the motor’s working environment, speed, load, and temperature.
The most common type is a ball bearing. In a ball bearing, steel balls roll between the inner and outer rings to reduce friction. The ball bearings are suitable for high speeds and low-load conditions. It is also estimated to be in common use on three-phase small and medium-sized motors. They run smoothly with low noise, thus their perfection in general industrial use.
The principle of the roller bearing is almost the same as the principle of the ball bearing, but instead of the balls, rollers are used which can support larger loads. Because the contact area between rollers and inner and outer rings is bigger, roller bearings can be suitable for heavy-load motors. These bearings are much used in industries where the procedures involve heavy-duty loads such as steel and mining.
Because of their self-aligning nature, spherical roller bearings can tolerate misalignment of the inner ring relative to the outer. Thus, a spherical roller bearing can continue to operate normally when the shaft is bent or when there is some misalignment in installation. These bearings are great for motors whose axes may slightly shift during operation and for construction machinery and power equipment.
Thrust bearings are designed to accept mainly axial, or thrust, loads and are usually used in applications with vertically mounted motors. Ideally, the thrust bearings prevent axial displacement of the rotor; this is where stability and smoothness come in during high-speed rotation.
Magnetic bearings are a special sort of bearing that uses electromagnetic forces to levitate the rotor between the stator without actual mechanical contact and friction. Nowadays, this technology is used in those highly demanding areas related to precision and high speed where neither loss nor failure can be afforded, such as aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing. However, considering the high cost, it always adopts in special situations. In this regard, different bearing mounting operations would result in different bearings performances. Therefore, basic principles of bearings mounting must be noticed to guarantee the operation performance of the bearings.
Bearing Placement
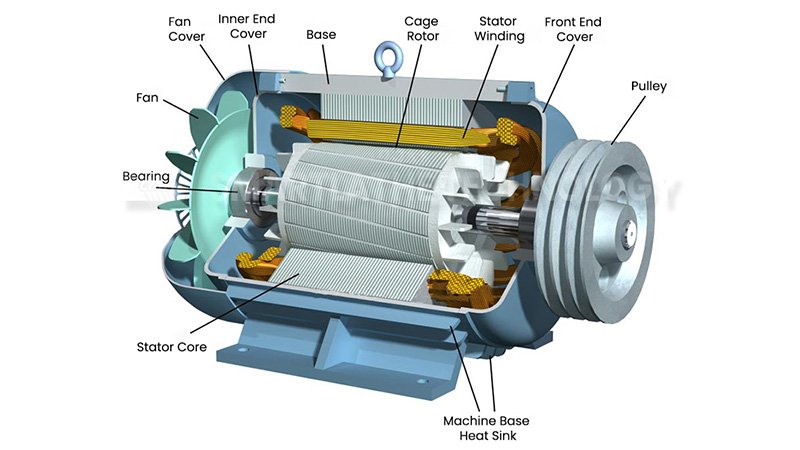
The bearings are normally mounted in a three-phase motor on the two end caps of the motor at each end of the rotor. With such an arrangement, the bearings will be able to support the weight of the rotor and withstand the radial and axial forces developed in the operation. Such dual-end bearing arrangement keeps the rotor in proper concentricity relative to the stator, avoiding friction between the rotor and stator that causes wear and energy losses.
Inside some high-power or special application motors, additional intermediate bearings can be added inside the motor for further improvement of rotor support. This bearing arrangement is usually applied to motors with longer shafts or special motors which must bear higher load, thus making rotation stable even when the length of the rotor is big.
The thrust bearings usually take the axial weight of the rotor in vertically mounted motors. Since the rotor is under the force of gravity, there will be considerable axial pull in the vertical direction. Thrust bearings keep the rotating part stable in this direction. Motors mounted vertically are normally used in applications involving pumps, elevator drives, and other similar applications that have to work under vertical axial conditions.
Common Issues
Of the parts in motors, bearings are the most failure-prone. Statistics show that bearing failures constitute about 60% of the failures of motors. Some of the common issues which different types of bearings face include those related to problems in lubrication, wear, overheating, contamination, and incorrect installation.
The most frequent cause that can result in bearing failure is improper lubrication. The inner structure of the bearing involves rings and rolling elements that have to be lubricated for friction reduction. In case of insufficient lubrication, overheating may accelerate wear and hence cause failure. On the other hand, over-lubrication leads to problems. Too much lubricant may develop too much pressure inside the bearing, increasing the level of friction, sometimes even damaging the seal and hence causing leakage of the lubricant.
In fact, bearing wear is inevitable with long-time and high-loaded motors. Friction gradually cuts down the rolling elements and rings. Too much wear can lead to abnormal vibrations and noise of the motor. In extreme cases, it can also lead to a situation where the rotor and stator will come into contact, resulting in irreparable damage to the motor.
Generally, overheating occurs when there is excessive speed, overload, or inadequate lubrication. High temperatures also break down the lubricants, which can lower friction and provide virtually no separation between the rolling elements and rings, thereby grossly raising wear. Normally, it is considered that temperature should not surpass 70°C for bearings running under average loads. If this temperature is higher, it will oxidize the lubricant and lower the service life of the bearing.
The other common cause of bearing failure is ingress of contaminants. Dust, dirt, and metal shavings and other foreign substances entering the bearing can lead to the failure of lubricant, causing friction and wear to increase. Thus, the issue of bearings being clean and well-sealed is of utmost importance.
Poor installation is also one of the common causes of bearing premature failure. Excessive amount of force during installation could make the bearings deform or get damaged. Installation misalignment causes abnormal stress during operating, which leads to bearing failure.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance surely helps in extending the lives of motor bearings. First, bearings have to be lubricated regularly. Under normal conditions, depending on the working condition and environment where the motor has to work, lubrication should be done every selected number of hours. Generally speaking, bearings of motors need relubrication after every 500 to 1,000 hours of operation.
Besides lubrication, regular checking on the condition of bearings is equally important. By observing it for abnormal noise, overheating, or vibrations, faults can be noticed at their earliest stage. Also, if there is major wear or crack on the working surface of the bearing, it should be replaced right away before further deterioration.
In particular, bearing cleanliness prevents contaminants from going into the bearing. Using good quality seals assists in effectively blocking dust and dirt from entry into the bearing, especially for applications in harsh environments, and in turn extends its useful service life.
Meanwhile, bearings are to be installed correctly. In case of installation, professional tools are meant for the bearings, and any hammering or forcing is to be avoided. When the installation is completed, a trial run must be conducted so that the condition of the bearing is checked and for smooth operations.
Why It Matters
The conditions of the motor bearings have a decisive influence on the entire performance of the motor. It has been said in industrial surveys that 50-60% of cases related to motor failures pertain to bearings. In other words, it means that the health of the bearings influences the reliability and service life of the motor. Bad bearings would not only diminish the efficiency of the motor but might also result in major failure of the equipment, causing loss of time and money.
A good bearing can greatly reduce friction and energy losses and raise the efficiency in operation. Failure will, however, lead to overheating, increased vibration, wasting energy, and even further damage to other parts of the motor. Thus, the maintenance of bearings is an important task for the long-term efficient running of motors.
Moreover, regular bearing inspections and maintenance can extend the motor’s service life and minimize the failure rate, thus promoting efficiency in production. The cost of deterioration of industrial equipment is just too high. For continuously running production lines, a single faulty bearing will bring it to a full standstill. Therefore, bearings cannot be considered insignificantly serious as an important part of the motor. With effective maintenance, large amounts of money in repair and replacement can be saved for companies.