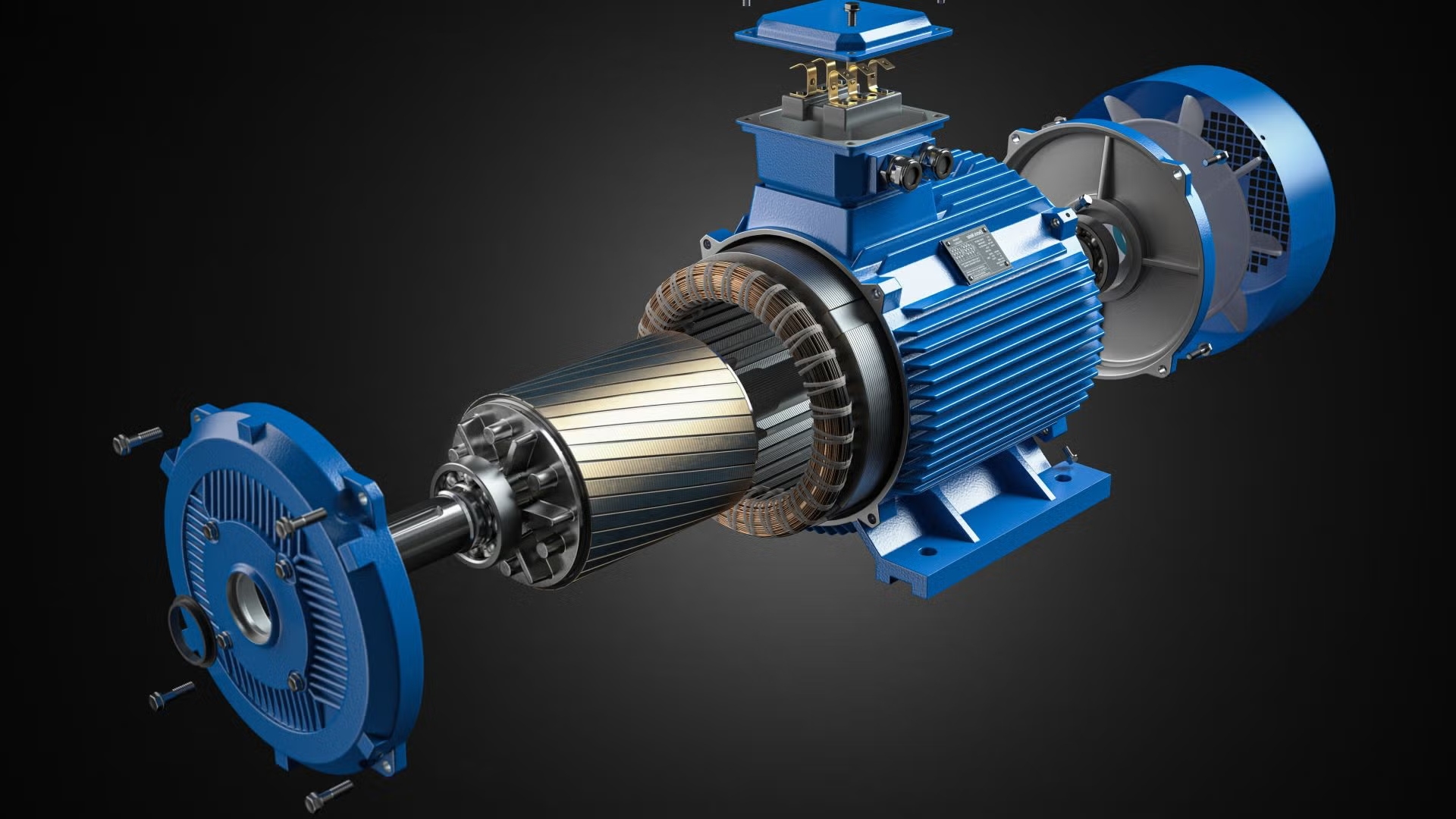
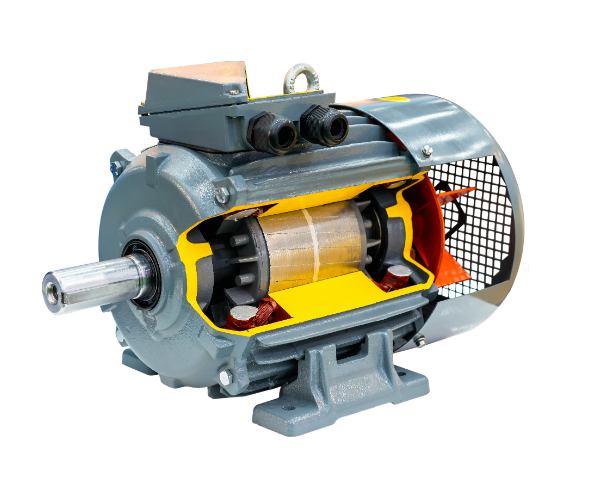
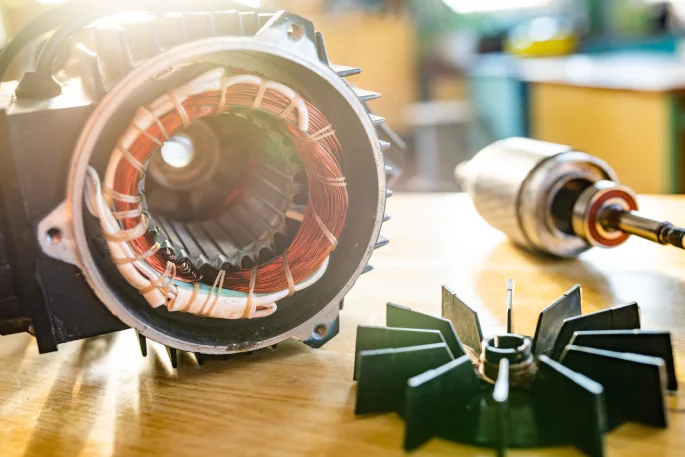
Generally speaking, three-phase motors are used for applications that require high power and efficiency. These applications include heavy machinery, HVAC systems, automated production lines, and water pump systems. Efficiency in three-phase motors reaches as high as 95% compared to single-phase motors, resulting in a reduction of energy consumption by about 15%. In industrial production, the use of three-phase motors ensures that equipment operates for long periods while failure rates are reduced. Lower startup current minimizes impact on the power grid. This makes the use of three-phase motors in long-term applications more economically viable, hence they are widely applied in major equipment found in factories and buildings.
Power Transmission in Industrial Equipment
Power transmission lies at the very center of the operation of any production line in industry. All these devices—large compressors, pumps, fans, machine tools, and hoists—demand continuous, powerful power support. According to the “Industrial Electrical Equipment Application Manual,” the operational efficiency of three-phase motors usually ranges between 90% and 95%, at least 10% higher than that of single-phase motors. This efficiency difference is very important in large-scale production, especially for equipment that runs for long periods.
Compressors are essential in many manufacturing industries. They require continuous power to compress gases, and when single-phase motors are used, it may result in significant current fluctuations and high energy consumption. Three-phase motors not only provide smooth power output but also effectively reduce fluctuations in current loads, hence keeping the equipment running smoothly and efficiently.
This means that equipment using three-phase motors can operate more than 30% longer than those equipped with single-phase motors in industrial settings, particularly in high-load working environments. Considering the high initial investment in industrial equipment, using three-phase motors can significantly reduce costs for maintenance or replacement, thereby increasing overall economic efficiency.
Building and HVAC Systems
Three-phase motors have become, for the most part, standard in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems of large buildings. In high-rise buildings and shopping malls, the long continuous operation of fans and water pumps in air conditioning systems requires a stable power supply from motors with high energy efficiency ratings.
Statistics show that the power consumption by air conditioners accounts for 30% to 50% of the total power consumption of a building. Efficient three-phase motors can effectively reduce the energy consumption of air conditioners by 10% to 15%. This is especially applicable in hot seasons when air conditioners tend to run nearly throughout the day, and low power consumption with long runtime reduces the electricity expenses of firms to a great extent.
Three-phase motors have a lower startup current compared to single-phase motors; due to this, their impact on the network is not as great at the time of equipment startup. This is very critical, especially in areas where the power supply is not stable; hence, these three-phase motors ensure that HVAC systems can run without shutdowns caused by voltage fluctuations.
Manufacturing and Automation
The manufacturing industry is becoming increasingly automated. In recent years, the rapid development of automated equipment has greatly enhanced production efficiency, placing higher demands on power systems. Three-phase motors, with their high efficiency and stability, have become the driving force of automated equipment.
The application of conveyor belt systems in production lines is another usage where long periods of operation and highly precise speed and position control are required. In such applications, three-phase motors are capable of outputting stable torque, allowing production lines to smoothly convey materials at constant speeds. According to market research, the failure rate of three-phase motors is about 40% lower than that of single-phase motors, which is very meaningful in terms of reducing downtime and increasing production efficiency.
Industrial robots are also one of the most important automated parts in manufacturing. The motors have to work under conditions requiring high precision and heavy loads, and three-phase motors can provide continuous power support to ensure the accuracy of robot movements. Especially in industrial scenarios that require high speed and frequency, three-phase motors boast superior stability and longevity compared with other types of motors.

Agricultural Machinery and Water Pump Systems
Most agricultural machinery works outdoors, such as irrigation systems and feed transporting equipment, which require high operating power. According to data from the Agricultural Machinery Equipment Manual, three-phase motors applied in the equipment not only improve power output efficiency but also extend the service life of the machinery.
Irrigation system water pumps usually operate continuously for hours or even days under heavy loads. Especially during dry spells, pumps may operate continuously for up to 24 hours. The efficiency of three-phase motors greatly lowers the power consumption of the equipment. For instance, hourly energy consumption is roughly 20% less compared to single-phase motors. In addition, three-phase motors are more durable in supporting changing outdoor weather, decreasing the occurrence of motor damage caused by harsh environments.
This is usually because agricultural equipment is set up far from urban power grids, and the use of three-phase motors ensures that the machines have a stable power output even over long-distance power transmission. This is among the major reasons why three-phase motors are extensively used in agriculture.
Ships and Heavy-Duty Vehicles
Extensive applications of three-phase motors can also be found in ships and heavy-duty vehicles, particularly in propulsion systems for ships and power systems for large vehicles. Ships and heavy-duty vehicles often require continuous high-power output, and thus three-phase motors are mainly applied to these devices.
An example of this is ship propulsion systems, where the main propulsion system needs to operate efficiently on long voyages. The use of three-phase motors during propulsion ensures powerful propulsion in a stable manner with reduced fuel consumption. According to the “Maritime Equipment Energy Saving Report,” three-phase motor propulsion systems reduce fuel consumption in ships by about 15%, which is important and can cut operating costs for shipping companies.
Therefore, three-phase motors with high power density and stability are employed in heavy-duty vehicles such as trains and mining trucks, making them indispensable in the traction systems of such vehicles. In mines and construction sites where long-term heavy-duty operation is common, three-phase motors provide steady power support for continuous operation, reduce equipment failure rates, and cut down maintenance costs.