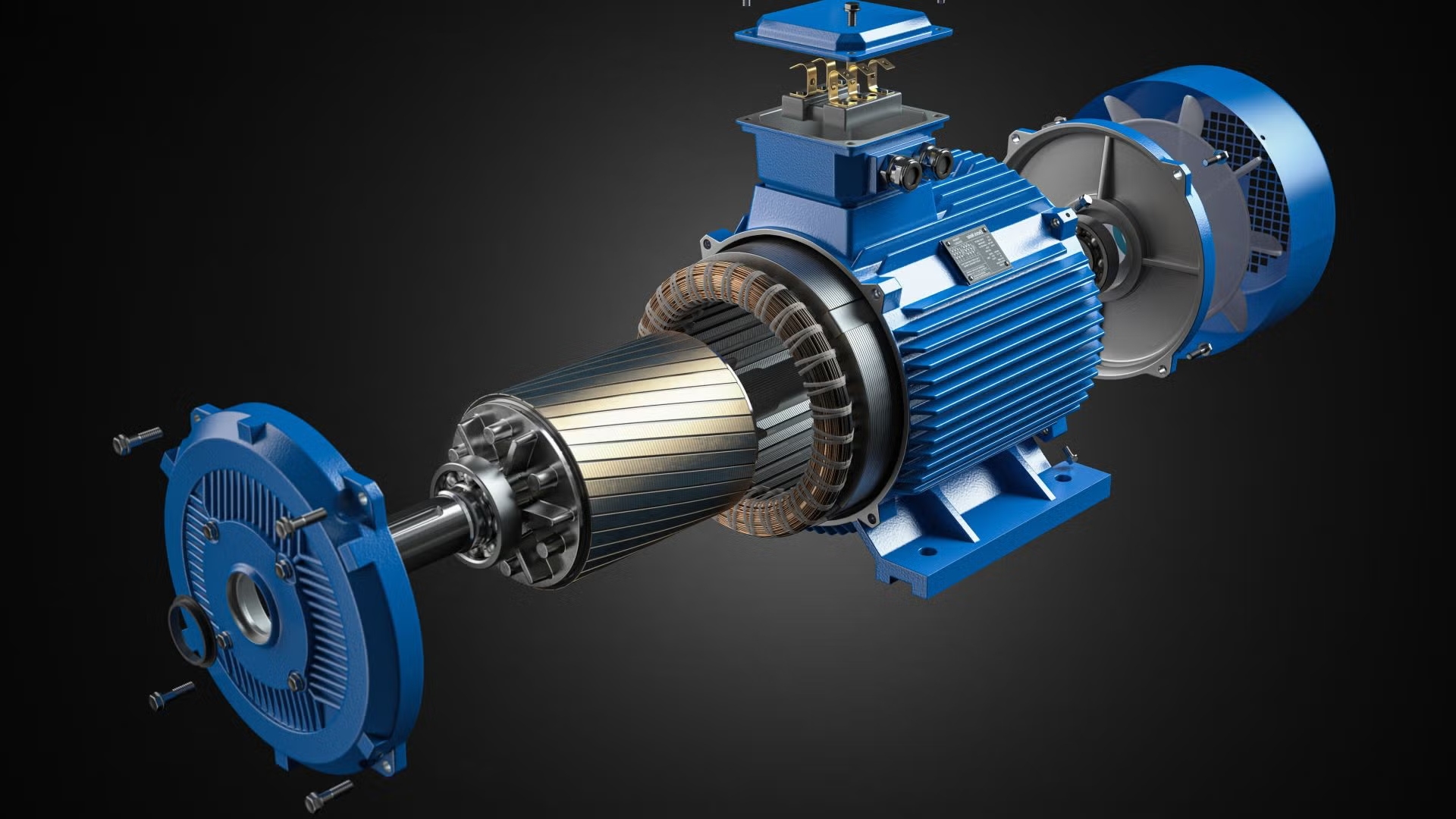
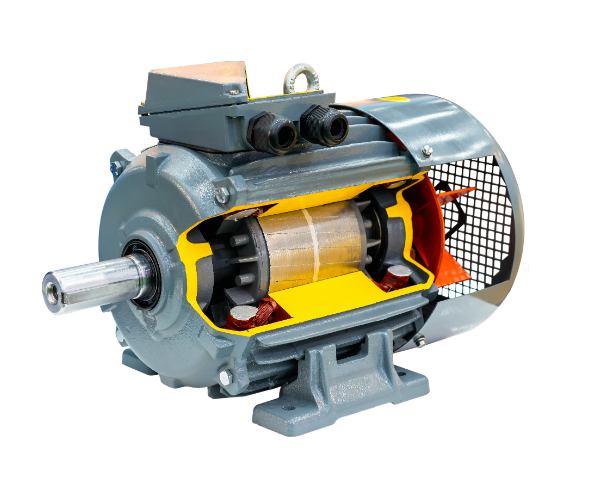
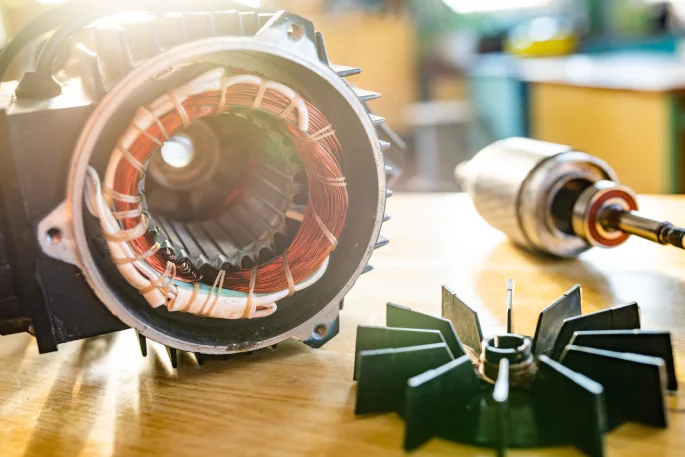
Because of its high efficacy, strong load resistance and stable operation, the 3-phase motor is often used in industry. Three-phase induction motors are generally 15% more efficient than single-phase induction motors, which saves some electricity and is especially suited for high-power implementations like fans and compressors. Also, the vibration amplitude of three-phase motors rarely exceeds values greater than 0.02mm/s², enabling smoother performance and reducing wear on equipment. The three-phase one has almost 2 times the start torque of a single-phase motor and ease of maintenance on an average life cycle time limit of up to 15 years, which makes the long-term operation costs decrease.
High Efficiency, Lower Operating Costs
In high-power industrial applications, three-phase motors are more efficient than single-phase motors. Three-phase motors are generally considered to divide up the global efficiency standards IE3 or even LO4 and the associated green of innovative technology levels, which easily exceed 20% of standard motor green values. By replacing all of its equipment with IE4-standard three-phase motors, the annual electricity cost of a major manufacturing plant fell by about 12%, representing savings in excess of 1 million USD. This is because three-phase motors distribute current more evenly, which minimizes power loss and lowers long-term operational costs.
Operating the crusher using a 3-phase motor also eliminates additional heat generated from hydraulic pumps that would have normally been required. Three-phase motors used in large compressor systems are highly energy-saving, up to 95%, and are widely deployed in petrochemical plants. This means that after 1,000 hours of operation, only 50 of those go to waste as heat rather than light which greatly reduces the load on cooling systems in addition to consuming less electricity.

Greater Output Power, Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications
Three-phase motors work very well in mechanical installations, as industrial equipment usually requires continuous high-load operation. With a single-phase, maximum loading, the efficiency of a 100kW three-phase machine can be as high as 110%, but with single-phase at the same time, it is usually restricted to a rather less efficient, up to about 80%. Three-phase motors find use in high-capacity load situations, such as large fans, pumps, compressors, and mechanical industrial equipment.
In the case of mining, this means that three-phase motors can endure 24-hour heavy-duty running on ore crushers, for example, with a mean time between failure (MTBF) or up to 25000 hours. By comparison, the average MTBF for single-phase motors is approximately 8,000 hours, so three-phase motors support longer periods of continuous work to reduce the loss of production as a result of interruptions.
Smooth Operation, Low Vibration
Three-phase motors can generate a continuous rotating magnetic field, avoiding the vibration and noise issues caused by uneven magnetic fields. Experimental data shows that the vibration amplitude of three-phase motors under rated load is typically less than 0.02mm/s², while the vibration amplitude of single-phase motors approaches 0.08mm/s². In steel production, large rolling mills require extremely smooth operation, or else product precision may suffer. Using three-phase motors can control this error to within 0.05mm, ensuring the product meets high standards.
Low vibration also means a significant reduction in mechanical wear. After a car manufacturing plant fully adopted three-phase motors on its production lines, the replacement cycle of mechanical parts was extended by 35%, significantly reducing maintenance costs and downtime.

High Starting Torque, Excellent Starting Performance
The starting torque of three-phase motors is commonly over twice as great as that of single-section motors. For applications needing high starting torque, like conveyor belts and elevators, three-phase motors can be well utilized in handling frequent start-stop operations. Single-phase motors usually require a current peak of up to 3 times the operating current (3 to 7.5 times the nominal torque), presenting one problem, as they overload and damage electrical equipment.
At a port, high-power three-phase motors drive the swivel movements of cranes using an electric drive system that can be designed to achieve a full start-up under load in only 4 seconds. Conventional single-phase motors, however, are greater than 10 sec, and continuous driving capability is disturbed by thermal protection that is triggered without reason.
Simple Maintenance, Long Service Life
Three-phase motors have a basic structure and also need less maintenance on a regular basis. The typical three-phase motors usually last about 15 years in normal operation before replacement becomes a consideration, while the single-phase motors are generally replaced every 8 to 10 years. A steel plant has published the service information of its three-phase and single-phase motors, and data reveals that out of a total machine cost, the annual maintenance on the same would account for about 1.2%, whereas in the case of a single-phase motor, this is quite close to 3%.
Not having to service your gear as often will also mean that you are not left with downtime doing maintenance work. The average failure rate of three-phase motors in large pulp mills is as low as 0.3% per year, which effectively reduces downtime caused by failures and ensures the stability of production processes. In three-phase motors, the high current and mechanical stress they must handle is spread out among their components, which allows for more heavy-duty designs of elements such as bearings and winding systems or increased service lifespan.